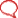
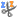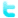Diabetic Kidney Disease, Animation
diseases Tags: Animation, Diabetic, Disease, KidneyNo Comments »
DKD, or diabetic nephropathy: pathophysiology, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis and management. For patient education. This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com/-/galleries/narrated-videos-by-topics/diabetes/-/medias/0079bcc6-2a8f-48d6-947d-57b464d2e271-diabetic-kidney-disease-narrated-animation
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Voice by : Marty Henne
Support us on Patreon and get early access to videos and free image downloads: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Diabetic kidney disease, or diabetic nephropathy, is kidney disease caused by diabetes. It’s a very common diabetic complication, affecting about one third of people with diabetes type 1, and half of those with diabetes type 2. Diabetic kidney disease is responsible for most of the excess mortality associated with diabetes.
Because the kidneys remove metabolic wastes, control blood pH, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, as well as produce several hormones; loss of kidney function results in accumulation of toxic wastes, electrolyte imbalances, and a number of other health problems.
The disease develops slowly over time, progressing from renal insufficiency to end-stage renal failure. Often, initial loss of renal tissue does not produce any symptoms. Symptoms typically appear when a significant portion of kidney function is already lost. The ability to concentrate urine is usually the first to be impaired, resulting in frequent trips to the bathroom, especially at night. Other early signs include fatigue, loss of appetite, and decreased mental ability.
Chronic high blood glucose levels, together with high blood pressure caused by diabetes, bring damage to tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, affecting their functions. Cellular degeneration in the functional units of the kidneys, the nephrons, in particular the podocytes of renal glomeruli, further contributes to the impairment of renal functions.
Diabetes, especially when poorly managed, is the biggest risk factor for chronic kidney disease. Other risk factors are the same as those for high blood pressure and include smoking, having high cholesterol levels, and being overweight.
Because initial loss of renal tissue does not produce any symptoms, it is important for diabetic patients to test annually for kidney functions. The tests typically include blood and urine analysis.
Prevention and management strategies consist of controlling blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels; all of which can be achieved with a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
Lifestyle measures typically include a healthy diet with low salt intake, increased physical activity, weight management, and smoking cessation.
Among all blood pressure lowering medications, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers, which block the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, work best to protect kidney functions.
End-stage kidney disease requires dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Chronic Kidney Disease | CKD | kidney disease symptoms | kidney failure | how to reverse kidney disease | kidney disease prognosis | kidney disease signs
10 signs and symptoms of chronic kidney diseases, and 9 measures to lower your risk.
Chronic kidney disease is a progressive condition. Chronic kidney disease is more prevalent in older individuals, women and in people experiencing diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
Sign and symptoms that may be seen in kidney diseases:
Tiredness, having less energy or having trouble concentrating.
Trouble sleeping
Dry and itchy skin
Urge to urinate more often
Blood in your urine
Your urine is foamy
Puffy eyes
Swollen ankles and feet
Poor appetite
Muscle cramping.
Few Golden Rules of Prevention to lower your chances of getting kidney disease are:
1. Getting regular check-ups with 2 simple tests: a urine test and blood test. A urine test called albumin creatinine ratio (ACR). A blood test called glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
2. Maintaining Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can damage your kidneys and increase your chances of getting kidney disease.
3. Manage Blood Sugar
High blood sugar levels can cause blood vessels inside the kidney to become narrow and clogged and can cause damage to the blood vessels and harm the kidneys.
4. Eat a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet can help lower blood pressure and blood lipids (fat in the blood).
5. Exercise
Exercise can help you keep a healthy weight, control blood pressure and cholesterol, build strength and endurance, and lower your chances of getting kidney disease.
6. Quit Smoking
Smoking causes diseases in every organ of the body, including the kidneys.
7. Do not overuse medicines:
Using too much pain medicine like NSAIDs may cause kidney disease.
8. Limit alcohol intake:
Alcohol increases your blood pressure. The extra calories in it can make you gain weight, too
10. Ask your health care provider the few questions about your kidney health that are mentioned in our video.
#kidneydisease
#kidneyhealth
#chronickidneydisease
#kidney
Medical disclaimer: Medinaz Academy does not provide medical advice. The content available in our books and videos, on our website, or on our social media handles do not provide a diagnosis or other recommendation for treatment and are not a substitute for the professional judgment of a healthcare professional in diagnosis and treatment of any person or animal. We intend to provide educational information only. The determination of the need for medical services and the types of healthcare to be provided to a patient are decisions that should be made only by a physician or other licensed health care provider. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you have regarding a medical condition.